This is especially true in the field of low cost residential PV inverters where efficiencies are used as major selling arguments. Traditional converter topologies to date reach their limitations and new approaches are necessary. Therefore, research areas are typically focusing on both new topologies and utilizing more advanced semiconductor devices.
To this end, semiconductor devices made of Silicon Carbide have been gaining increasing interest in the last two decades after the successful commercialization of high voltage power diodes. By now, the performance potential of switching devices made of Silicon Carbide is commonly accepted, though they have not found commonplace usage within commercial converter systems for several reasons, among others reliability, availability/cost and gate driver complexity. Therefore, more complex converters can be used instead to achieve lower semiconductor losses.
The contributions are:
- Comprehensive loss analysis and identification of major loss contributors within T-Type inverter and rectifier operation context
- Evaluation of the use and loss benefits of Silicon Carbide switching devices in the T-Type structure
- Thorough investigation of the Hybrid-Neutral-Point-Clamped (H-NPC) as an alternative for the Silicon Carbide based T-Type converter
- Alternative methodology of semiconductor loss model validation by experimental means
Figure 1: Double pulse test circuit for switching energy measurements
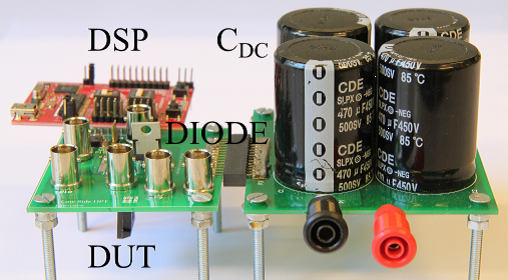
Figure 2: Photograph of the laboratory prototype of three-level inverter
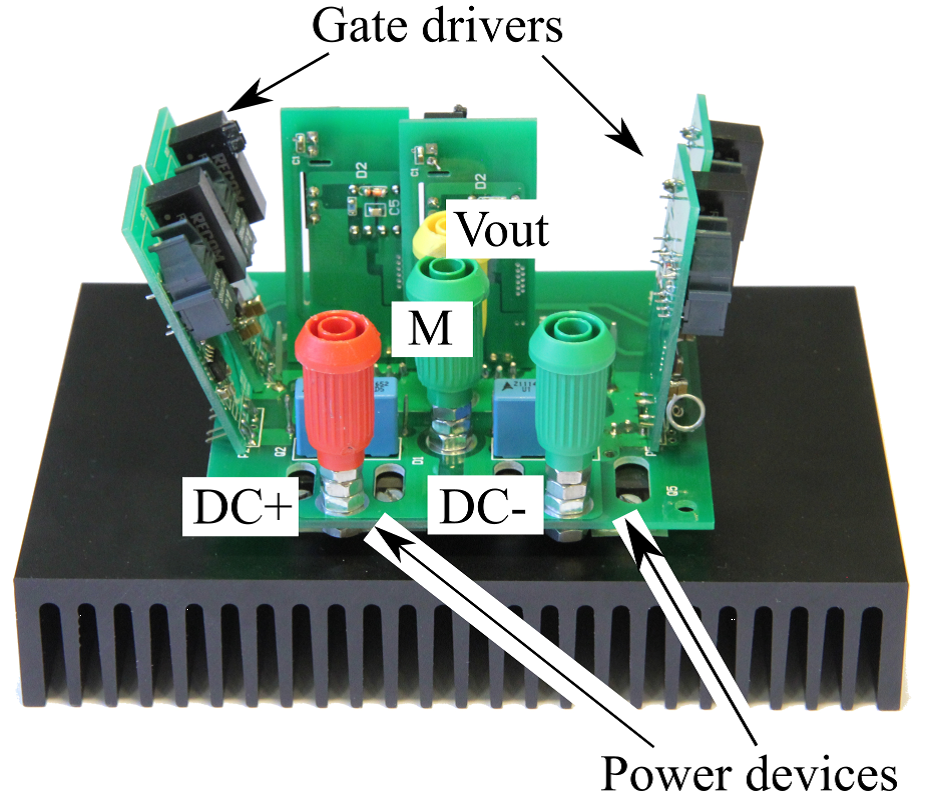
Figure 3: Experimental waveforms of the inverter operating at full load
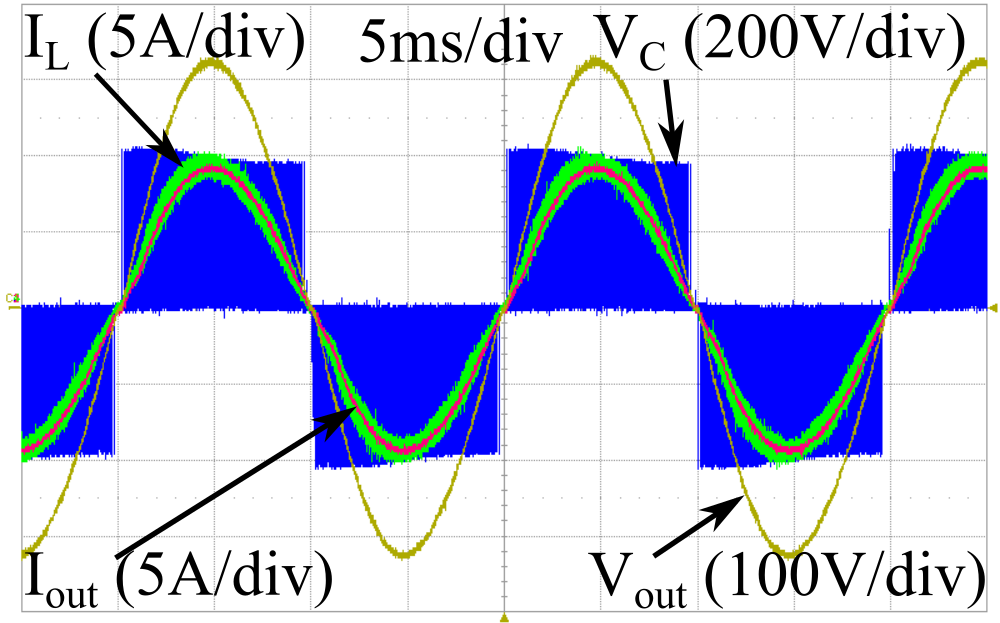
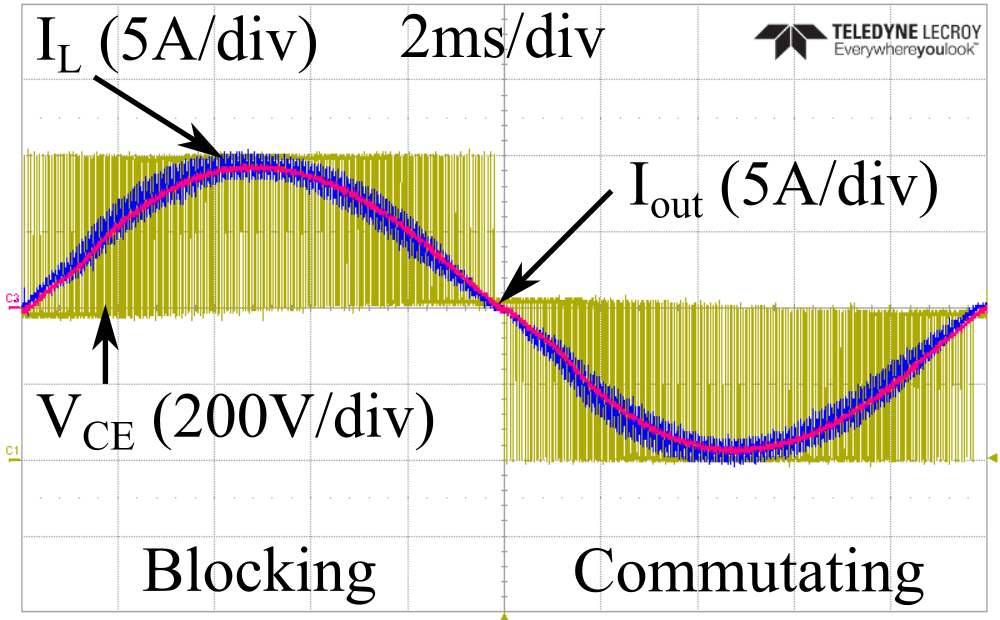
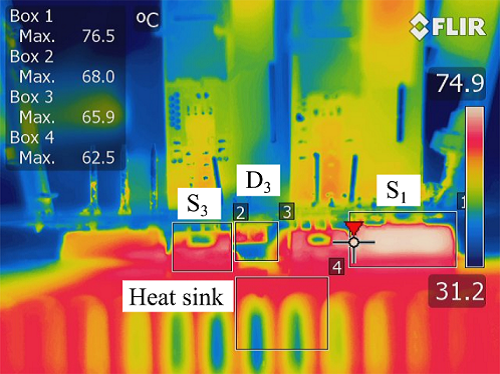
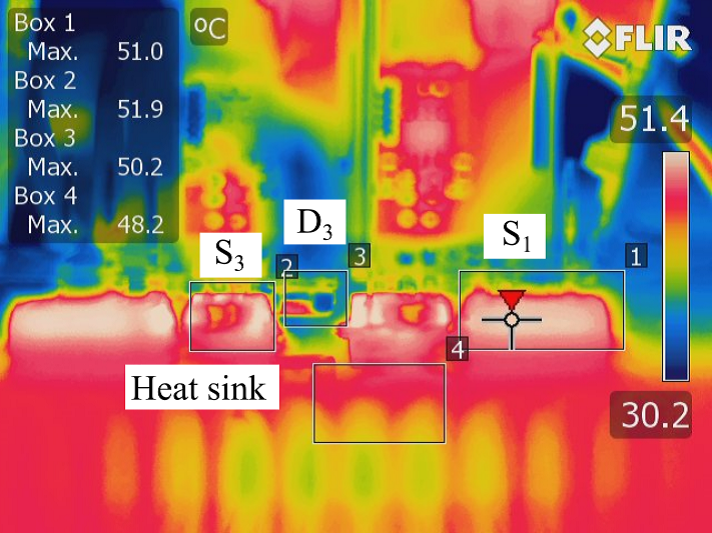
Figure 4: Case temperature measurements for the Si and SiC alternative
Contact Person

Zhe Zhang
Associate Professor
Technical University of Denmark
E-mail: zz@elektro.dtu.dk
